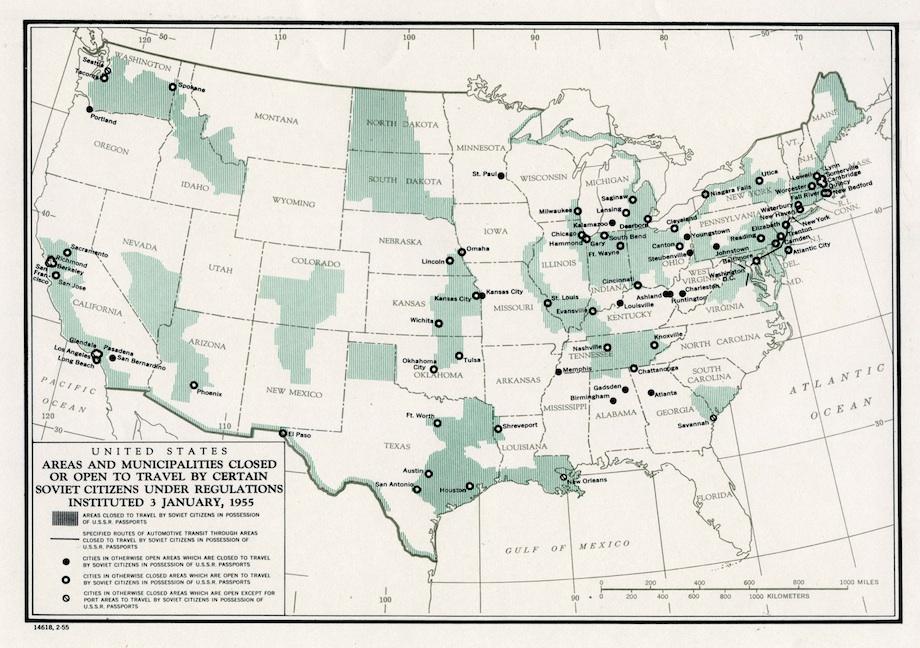
Slate’s new history vault published a gem from the Cold War last week. This map from January 1955 shows the areas in the United States that Soviet citizens could not travel.
This map shows where Soviet citizens, who were required to have a detailed itinerary approved before obtaining a visa, could and could not go during their time in the United States. Most ports, coastlines, and weapons facilities were off-limits, as were industrial centers and several cities in the Jim Crow South.
These restrictions mirrored Soviet constraints on American travel to the USSR. Both the United States and the Soviet Union had closely controlled the movement of all foreign visitors since World War II. A 1952 law in the U.S. barred the admission of all Communists, and therefore of Soviet citizens. (An exception was made for government officials.)
The Soviets’ decision to relax their controls after Joseph Stalin’s death in March 1953 left the U.S. open to charges that it, not the USSR, was operating behind an Iron Curtain. President Eisenhower and his foreign policy advisers decided to mimic Soviet policy as closely as possible: As of early 1955, citizens of either nation could enter approximately 70 percent of the other’s territory, including 70 percent of cities with populations greater than 100,000.
As a North Dakota native, my first question was why prohibit travel to all of western North Dakota and most of South Dakota? (hint: it’s probably not what you think…)
My initial thought was that restrictions were in place in the region because the area is home to two SAC bases — Ellsworth Air Force Base outside of Rapid City in western South Dakota and the Minot Air Force Base in north central North Dakota. The area was also littered with ICBM silos. As a kid, I remember the daily training runs of the B-52s overhead and perhaps the restricted area included the training flight paths.
But this explanation doesn’t seem to fit. First, the airbases did not take on the B-52s until the late 1950s and the ICBMs were not deployed until the early 1960s. True, but weren’t the plans in place in 1955 to deploy both B-52s and ICBMs to the region — so maybe the restrictions were anticipatory? Yes, but then why doesn’t the map include restrictions on access to north eastern North Dakota near Grand Forks (another SAC base) and Devils Lake — one of the largest ICBM fields? And why doesn’t it restrict access to south-eastern Wyoming and western Nebraska near Warren AFB? Hmmm.
Since several cities in the Jim Crow south were off limits, it seems more likely that the travel ban on the Dakotas was motivated by similar concerns — the area is home to several Native American reservations: Fort Berthold, Standing Rock, Cheyenne River, Pine Ridge, Crow Creek, Rosebud, and Yankton. The timing of the map in 1955 corresponded with the U.S. government’s highly contested termination policy which intended to grant Native Americans rights of American citizenship but end tribal sovereignty and tax exemption and close the Indian reservations and sell off property and resources. At the time, the Soviets were countering criticism of their human rights records by proclaiming their support for African Americans and Native Americans. The Native American reservations were seen by conservative backers of the termination policy as a form of socialism and communism and there were plenty of hyped up fears that the Soviets would exploit and facilitate Native American resistance to the termination policy and foment anti-government agitation.
This is all a bit speculative. I’m curious if anyone has further insights.
Jon Western has spent the last fifteen years teaching IR in liberal arts colleges at Mount Holyoke College and the Five Colleges in western Massachusetts. He has an eclectic range of intellectual interests but often writes on international security, U.S. foreign policy, military intervention, and human rights. He occasionally shares his thoughts about professional life in liberal arts colleges. In his spare time he coaches middle school soccer, mentors the local high school robotics team, skis, and sails.


It seems an interesting map; Soviet citizens couldn’t travel to the part of the country I grew up in, but they could travel to the city I grew up in ….
My guess is that it had to do with mapping areas for targeting. You could visit cities because there was no harm, but allowing Soviets to travel throughout those regions would let them figure out exactly where targets were/could be. Note that many such areas are important centers of industrial and agricultural production.
PM, the prime agricultural production area in North Dakota is in the Red River valley in the eastern part of the state. It also doesn’t explain why prime agricultural real estate in Minnesota, Iowa, and Nebraska isn’t restricted.
Overlay the map with the nuclear weapons complex and important military installations and most of it will make sense.
The point of the post is that this argument doesn’t make sense. Several major SAC bases and ICBM fields are not included as restricted zones. And, the map predates the SAC bases and ICBM installations in the western Dakotas.
Not all military interests are SAC bases or ICBM farms. For example, Badlands Bombing Range. Ellsworth AFB was the site of an early warning radar system in the 1950s. Etc. etc. Much of the map matches up with the weapons complex–Oak Ridge, Savannah River, Pantex. In the southwest, Los Alamos, White Sands, Nevada Test Site. Rocky Flats in Colorado. Kansas City. Dayton, Ohio. Southern Idaho, Hanford. It wouldn’t surprise me if some areas are false flag, to confuse the Soviets.